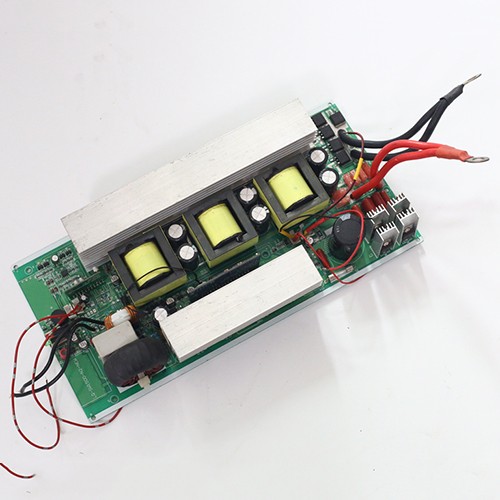
Special board PCB
Special board PCB is mainly used in special application scenarios such as high frequency and high reliability.
Special board types:
1. High frequency materials: such as Panasonic's Megtron 6, Rogers3003/RT5880, etc., suitable for high frequency signal transmission.
2. Composite substrates: such as the CEM series, which combines the advantages of paper base and glass fiber cloth base.
Special board PCBs are classified according to the special materials or performance they use. Common special boards include but are not limited to the following:
1. High Tg PCB:
Tg (glass transition temperature) is an important indicator to measure the heat resistance of PCB board. 1. Metal-based PCB: PCB with metal (such as aluminum, copper, etc.) as the base material has excellent heat dissipation performance and mechanical strength, and is suitable for high-power and high-heat electronic devices.
3. Ceramic-based PCB:
PCBs using ceramic materials as substrates have extremely high heat resistance, corrosion resistance and electrical insulation properties, and are suitable for electronic equipment in extreme environments.
4. Flexible PCB (FPC):
PCB with polyimide or polyester film as the base material has the characteristics of being bendable and foldable, and is widely used in wearable devices, medical devices, automotive electronics and other fields.
5. High-frequency PCB:
PCB designed for high-frequency signal transmission is made of low-loss materials to reduce signal attenuation and interference during transmission, and is suitable for wireless communications, radars, satellites and other fields.
6. Halogen-free PCB:
PCB made of halogen-free materials meets environmental protection requirements, reduces pollution to the environment, and is suitable for application scenarios with high environmental protection requirements.
Special board PCBs usually have one or more of the following characteristics:
1. Excellent performance: such as high temperature stability, high heat dissipation, high electrical insulation, etc., to meet the performance requirements of specific application scenarios.
2. Special functions: such as bendability, high-frequency transmission capability, etc., to achieve functions that traditional PCBs cannot accomplish.
3. Environmental protection: Made of environmentally friendly materials to reduce the impact on the environment
Special board PCBs are classified according to the special materials or performance they use. Common special boards include but are not limited to the following:
1. High Tg PCB:
Tg (glass transition temperature) is an important indicator to measure the heat resistance of PCB board. 1. Metal-based PCB: PCB with metal (such as aluminum, copper, etc.) as the base material has excellent heat dissipation performance and mechanical strength, and is suitable for high-power and high-heat electronic devices.
3. Ceramic-based PCB:
PCBs using ceramic materials as substrates have extremely high heat resistance, corrosion resistance and electrical insulation properties, and are suitable for electronic equipment in extreme environments.
4. Flexible PCB (FPC):
PCB with polyimide or polyester film as the base material has the characteristics of being bendable and foldable, and is widely used in wearable devices, medical devices, automotive electronics and other fields.
5. High-frequency PCB:
PCB designed for high-frequency signal transmission is made of low-loss materials to reduce signal attenuation and interference during transmission, and is suitable for wireless communications, radars, satellites and other fields.
6. Halogen-free PCB:
PCB made of halogen-free materials meets environmental protection requirements, reduces pollution to the environment, and is suitable for application scenarios with high environmental protection requirements.
Special board PCBs usually have one or more of the following characteristics:
1. Excellent performance: such as high temperature stability, high heat dissipation, high electrical insulation, etc., to meet the performance requirements of specific application scenarios.
2. Special functions: such as bendability, high-frequency transmission capability, etc., to achieve functions that traditional PCBs cannot accomplish.
3. Environmental protection: Made of environmentally friendly materials to reduce the impact on the environment